Vehicle
Manage two threaded connections between a Qt gRPC™ client and a C++ gRPC server.
The example simulates a vehicle dashboard that displays data sent by a gRPC server.
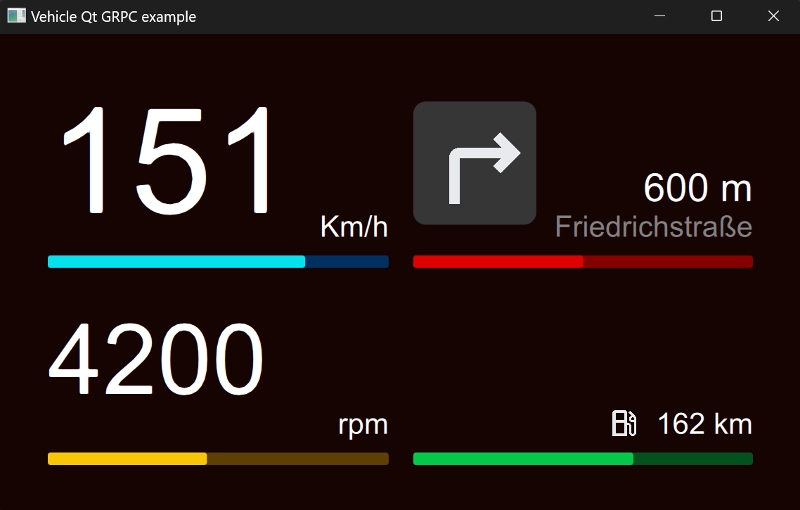
The example code has the following components:
vehicle_clientQt gRPC client application that uses the qt_add_protobuf() and qt_add_grpc() CMake functions for message and service Qt code generation.vehicle_serverapplication that calls C++ gRPC plugin for generating server code and implementing simple server logic.
Note: you need the C++ gRPC plugin installed. Find details here: Module prerequisites
Both components use generated messages from the protobuf schemas described in the files vehicleservice.proto and navigationservice.proto.
Vehicle service:
message SpeedMsg {
int32 speed = 1;
}
message RpmMsg {
int32 rpm = 1;
}
message AutonomyMsg {
int32 autonomy = 1;
}
service VehicleService {
rpc getSpeedStream(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (stream SpeedMsg) {}
rpc getRpmStream(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (stream RpmMsg) {}
rpc getAutonomy(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (AutonomyMsg) {}
}
Navigation service:
enum DirectionEnum {
RIGHT = 0;
LEFT = 1;
STRAIGHT = 2;
BACKWARD = 3;
}
message NavigationMsg {
int32 totalDistance = 1;
int32 traveledDistance = 2;
DirectionEnum direction = 3;
string street = 4;
}
service NavigationService {
rpc getNavigationStream(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (stream NavigationMsg) {}
}
The VehicleManager C++ singleton uses two QThread instances to communicate with the server in parallel. The threads have different gRPC connection types. In this example, there are two types:
- Server streaming RPCs For example, the speed stream of the vehicle thread. It uses two callback functions: QGrpcServerStream::messageReceived and QGrpcOperation::finished
Empty speedRequest; m_streamSpeed = m_client->getSpeedStream(speedRequest); connect(m_streamSpeed.get(), &QGrpcServerStream::messageReceived, this, [this]() { if (const auto speedResponse = m_streamSpeed->read<SpeedMsg>()) { emit speedChanged(speedResponse->speed()); } }); connect( m_streamSpeed.get(), &QGrpcServerStream::finished, this, [this](const QGrpcStatus &status) { if (!status.isOk()) { auto error = QString("Stream error fetching speed %1 (%2)") .arg(status.message()) .arg(QVariant::fromValue(status.code()).toString()); emit connectionError(error); qWarning() << error; return; } }, Qt::SingleShotConnection);
- Unary RPCs The RPC
getAutonomyoperation is a unary RPC. It returns a single response. It is only connected to the QGrpcOperation::finished signal.Empty autonomyRequest; std::unique_ptr<QGrpcCallReply> autonomyReply = m_client->getAutonomy(autonomyRequest); const auto *autonomyReplyPtr = autonomyReply.get(); connect( autonomyReplyPtr, &QGrpcCallReply::finished, this, [this, autonomyReply = std::move(autonomyReply)](const QGrpcStatus &status) { if (!status.isOk()) { auto error = QString("Call error fetching autonomy %1 (%2)") .arg(status.message()) .arg(QVariant::fromValue(status.code()).toString()); emit connectionError(error); qWarning() << error; return; } if (const auto autonomyMsg = autonomyReply->read<AutonomyMsg>()) { emit autonomyChanged(autonomyMsg->autonomy()); } }, Qt::SingleShotConnection);
The client main window interface is defined in the Main.qml file. It uses QML Connections type in order to connect to the signals of the VehicleManager C++ singleton to custom slots:
Connections {
target: VehicleManager
// This slot will be executed when the VehicleManager::totalDistanceChanged
// signal is emitted
function onTotalDistanceChanged(distance: int): void {
root.totalDistance = distance;
}
function onSpeedChanged(speed: int): void {
root.speed = speed;
}
function onRpmChanged(rpm: int): void {
root.rpm = rpm;
}
function onTraveledDistanceChanged(distance: int): void {
root.traveledDistance = distance;
}
function onDirectionChanged(direction: int): void {
if (direction == VehicleManager.RIGHT) {
root.directionImageSource = "qrc:/direction_right.svg";
} else if (direction == VehicleManager.LEFT) {
root.directionImageSource = "qrc:/direction_left.svg";
} else if (direction == VehicleManager.STRAIGHT) {
root.directionImageSource = "qrc:/direction_straight.svg";
} else {
root.directionImageSource = "";
}
}
After receiving a response, the client window updates the UI with the received data. This way, messages can be received in different threads and be sent to the client UI in a thread-safe way thanks to the signals.